Sleep apnea is a widespread sleep condition that’s marked by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep.
These interruptions can last for 10-30 seconds and may occur up to 30 times an hour, which can cause major disturbances to a patient’s sleep quality.
With 22% of men and 17% of women suffering from some form of sleep apnea, this condition is widespread enough that you may actually be acquainted with multiple people who have it.
In fact, reading this article could mean that you’re worried about some signs and symptoms that may indicate you have it too.
And if you do feel that you have sleep apnea, don’t worry. The disease is very treatable, especially if you recognise the signs of sleep apnea early on and act on it appropriately.
If you’re wondering whether you or a loved one has this condition, read on to learn more about the signs, symptoms, and treatment options for sleep apnea patients.
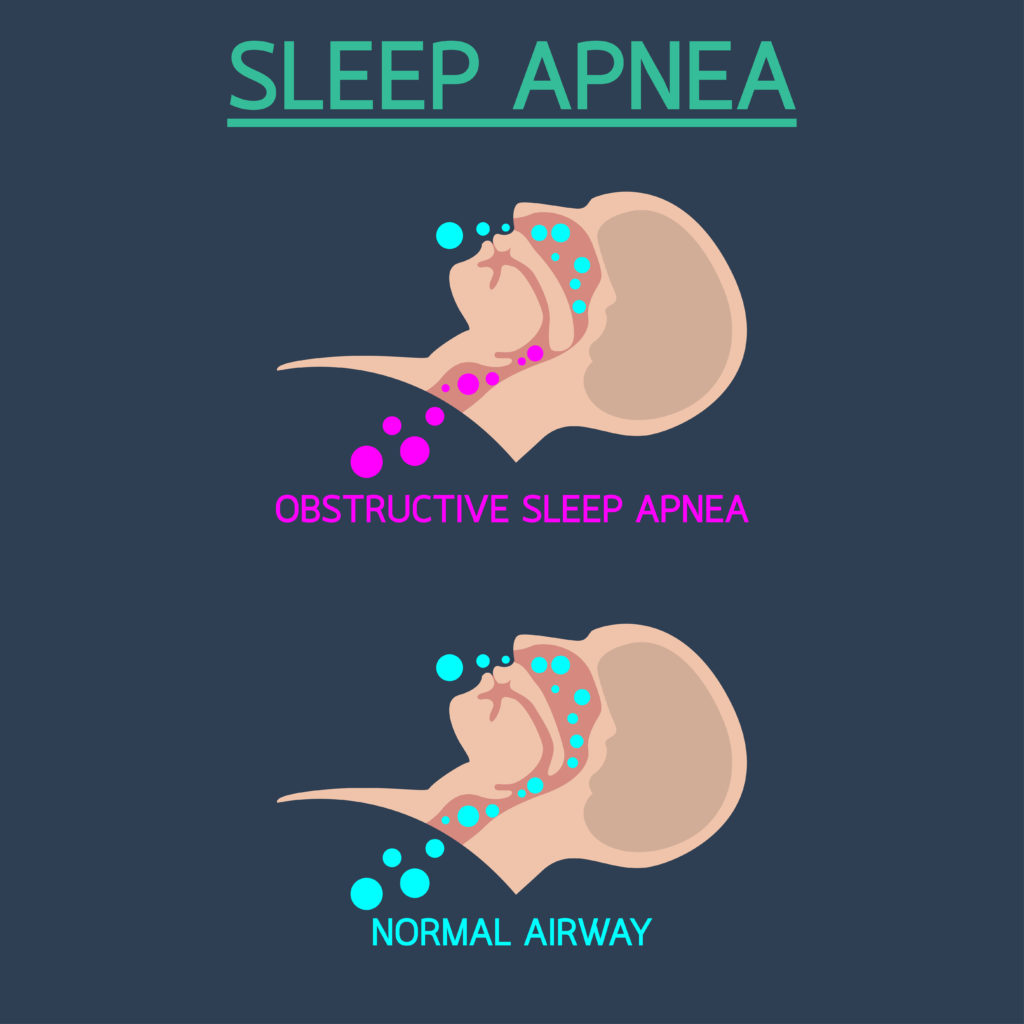
Image Credit: limestonedental
Contents
What is Sleep Apnea?
The word “apnea” is a Greek word, meaning breathless. The combination of sleep and apnea, therefore, indicates moments wherein a person is unable to properly breathe during sleep.
Sleep apnea is primarily caused by the unwanted relaxation of the airways, or the muscles at the back of the throat. These interruptions cut off the oxygen supply to the body and brain.
The lack of oxygen can cause sleep apnea patients to wake up during sleep. This disruption prevents them from sleeping straight, which can ruin their sleep quality and prevent them from reaping the benefits of restful sleep.
Types of Sleep Apnea
There are three primary forms of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and complex sleep apnea.
Each has unique characteristics that distinguish them from each other. Here they are in more detail:
Obstructive sleep apnea:
Also known as OSA, this form of sleep apnea is marked by a blockage of the upper trachea during sleep. This is the most common form of sleep apnea. This often occurs when an underlying condition narrows the airways, particularly obesity, tonsil enlargement, or hormonal problems.
Central sleep apnea:
This form of sleep apnea occurs because of a central nervous system dysfunction. The brains of people with CSA are unable to send signals to the body to breathe normally, causing the common signs of sleep apnea.
Complex sleep apnea:
Complex sleep apnea is a form of sleep apnea in which a person exhibits characteristics of both obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). People with this condition don’t respond well to OSA treatments like CPAP and may need further medical interventions.
Signs and Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can present itself differently from person to person. Furthermore, some symptoms can indicate which type of sleep apnea you have.
Here are some common signs and symptoms of sleep apnea:
- Loud and chronic snoring
- Choking, snorting, or gasping during sleep
- Long pauses in breathing
- Daytime sleepiness, regardless of the duration of nighttime sleep
- Waking up with a dry mouth
- Morning headaches
- Restless sleep
- Nighttime awakenings
- Difficulty concentrating during the day
- Mental health problems like depression
If you have any of these symptoms, whether one or multiple, it’s important to get a proper medical evaluation from a licensed medical professional.
While these symptoms don’t automatically mean sleep apnea, they do indicate underlying health problems that need to be addressed.
Getting a Diagnosis
If your quality of life has diminished greatly because of the condition, it’s important to schedule an appointment with a sleep specialist in a clinic.
These professionals will discuss your symptoms and medical history. They may also conduct special tests like nocturnal polysomnography to detect oxygen levels in your blood and your brain activity during sleep.
Based on the results from these tests, the doctor can figure out whether you have sleep apnea or not. They can also measure the severity of the condition.
From there, they’ll provide you with the appropriate treatment plan to get your health back on track. This can come in the form of both clinical and at-home treatments.
Treatment Plans to Manage Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can’t be cured. However, it can be managed to become less intense.
Once your doctor has diagnosed you with sleep apnea, they’ll create a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
The two primary clinical treatments a sleep apnea patient can undergo are CPAP treatment and surgery.
CPAP treatment involves the use of a special machine that releases a steady stream of pressurised air into your mouth using a mask. This mask is worn during sleep and helps keep the airways open, preventing sleep apnea and loud snoring. Check this page to see what CPAP masks are available right now.
In more severe cases, surgeries like uvulopalatopharyngoplasty or UP3 may be considered to open up the airways naturally. This procedure clinically removes the fat that surrounds the soft palate and pharynx, allowing you to breathe normally during sleep.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Sleep Apnea
Besides the aforementioned clinical treatments, certain lifestyle changes can significantly help manage sleep apnea.
Here are a few recommended lifestyle changes for sleep apnea patients.
Sleep on your side or abdomen:
Sleeping on your back can cause your tongue and soft palate to block your throat and prevent oxygen intake. You should consider sleeping on your side or abdomen instead.
Maintain a healthy weight:
Extra pounds can add fat around the neck area, obstructing your airways during sleep. Aim to lose weight, especially if you have a naturally high BMI.
Exercise regularly:
Regular physical activity can help remove fat in the body. Aim to get at least 150 minutes of moderate activity every week.
Limit alcohol and avoid smoking:
Alcohol relaxes the muscles in the throat. Smoking swells up your upper airway. Cut these habits to prevent the exacerbation of sleep apnea symptoms.
Use a humidifier:
Dry air can irritate the respiratory system. A humidifier can increase the moisture in your bedroom, which can promote better breathing throughout the night.
Sleep on schedule:
Having a disciplined sleep schedule can give you more hours to sleep at night, which may help make you feel lethargic during the day.
By abiding by these lifestyle changes, as well as following clinical treatments, you can reduce the intensity of sleep apnea to a more manageable degree.


